AI (ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE )
DEVELOPMENT OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE [ AI ] (BRIEF) –
A brief timeline of the past six decades of how AI evolved from its inception is described –
1956 – John McCarthy coined the term ‘artificial intelligence’ and had the first AI conference.
1969 – Shakey was the first general-purpose mobile robot built. It is now able to do things with a purpose vs. just a list of instructions.
1997 – Supercomputer ‘Deep Blue’ was designed, and it defeated the world champion chess player in a match. It was a massive milestone by IBM to create this large computer.
2002 – The first commercially successful robotic vacuum cleaner was created.
2005 – 2019 – Today, we have speech recognition, robotic process automation (RPA), a dancing robot, smart homes, and other innovations make their debut.
2020 – Baidu releases the LinearFold AI algorithm to medical and scientific and medical teams developing a vaccine during the early stages of the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic. The algorithm can predict the RNA sequence of the virus in only 27 seconds, which is 120 times faster than other methods.
AI [ ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ]

ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE contains two words – 1. ‘Artificial’ means “man-made” and 2. ‘Intelligence’ means “thinking-power”.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a set of technologies that enable computers to perform a variety of advanced functions, including the ability to see, understand and translate spoken and written language, analyze data, make recommendations, and more.
AI is the backbone of Artificial intelligence was founded as an academic discipline in 1956, and in the years since it has experienced several waves of optimism, followed by disappointment and the loss of funding (known as an “AI winter“), followed by new approaches, success, and renewed funding. AI research has tried and discarded many different approaches, including simulating the brain, modeling human problem solving, formal logic, large databases of knowledge, and imitating animal behavior. In the first decades of the 21st century, highly mathematical and statistical machine learning has dominated the field, and this technique has proved highly successful, helping to solve many challenging problems throughout industry and academia. documents, turns unstructured content into business-ready structured data, and unlocks valuable insights.
- Artificial intelligence is a field of science concerned with building computers and machines that can reason, learn, and act in such a way that would normally require human intelligence or that involves data whose scale exceeds what humans can analyze.
- AI is a broad field that encompasses many different disciplines, including computer science, data analytics and statistics, hardware and software engineering, linguistics, neuroscience, and even philosophy and psychology.
On an operational level for business use, AI is a set of technologies that are based primarily on machine learning and deep learning, used for data analytics, predictions and forecasting, object categorization, natural language processing, recommendations, intelligent data retrieval, and more.

Artificial intelligence was founded as an academic discipline in 1956, and in the years since it has experienced several waves of optimism, followed by disappointment and the loss of funding (known as an “AI winter”), followed by new approaches, success, and renewed funding. AI research has tried and discarded many different approaches, including simulating the brain, modeling human problem solving, formal logic, large databases of knowledge, and imitating animal behavior. In the first decades of the 21st century, highly mathematical and statistical machine learning has dominated the field, and this technique has proved highly successful, helping to solve many challenging problems throughout industry and academia.
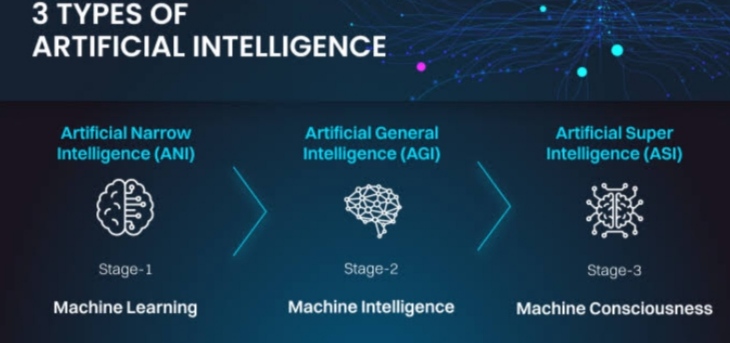
TYPES OF AI.
AI TYPE 1.
– Based on Capabilities.
1. NARROW AI [ ANI ] –

- Narrow AI or ‘ WEAK AI ‘ is a type of AI which is able to perform a dedicated task with intelligence.The most common and currently available AI is Narrow AI in the world of Artificial Intelligence.
- Narrow AI cannot perform beyond its field or limitations, as it is only trained for one specific task. Hence it is also termed as weak AI. Narrow AI can fail in unpredictable ways if it goes beyond its limits.
- Apple Siriis a good example of Narrow AI, but it operates with a limited pre-defined range of functions.
- Some Examples of Narrow AI are playing chess, purchasing suggestions on e-commerce site, self-driving cars, speech recognition, and image recognition.
2. GENERAL AI [ AGI ] –
- Artificial general intelligence (AGI) is defined as the intelligence of machines that allows them to comprehend, learn, and perform intellectual tasks much like humans. AGI emulates the human mind and behavior to solve any kind of complex problem.

Examples of AGI –
- Smart assistants (like Siri and Alexa)
- Disease mapping and prediction tools
- Manufacturing and drone robots
- Optimized, personalized healthcare treatment recommendations
- Conversational bots for marketing and customer service
- Robo-advisors for stock trading
- Spam filters on email
- Social media monitoring tools
- TV show recommendations from Spotify and Netflix
3. SUPER AI [ AGI ] –

Artificial superintelligence (ASI) is a hypothetical software-based system with intellectual powers beyond those of humans across a comprehensive range of categories and fields of endeavor. ASI doesn’t exist yet and is a hypothetical state of AI.
ASI is different from regular artificial intelligence (AI), which involves the software-based simulation of human intellectual capabilities, such as learning through the acquisition of information, reasoning and self-correction. AI is increasingly a part of our everyday lives in systems such as virtual assistants, expert systems and self-driving cars. Nevertheless, AI technology is in its early days of development. Systems vary in their abilities, but all current ones are examples of narrow AI or weak AI. They are high-functioning systems that replicate and even surpass human intelligence but only for a specific purpose.
